Low-E Glass
Low-E glass is designed to limit heat transfer in commercial, industrial, and domestic settings, leading to improved indoor comfort and reduced energy costs.

Introduction to Low-E Glass
Low-E glass is designed to limit heat transfer in commercial, industrial, and domestic settings, leading to improved indoor comfort and reduced energy costs. Engineered with ultra-thin layers of metal oxides, Low-E glass reflects infrared (IR) light while permitting visible light to pass through, effectively minimizing heat transfer. Essential to modern architecture and green building technology, Low-E glass significantly boosts energy efficiency. Discover the comprehensive benefits, diverse types, and versatile applications of Low-E glass in this detailed review, and see how it contributes to a more sustainable environment.

Characteristics of Low-E Glass
Low-E glass offers a unique capability to control heat transfer, making it an exceptional choice for various applications. Additional key features include:
Thermal performance
U-value: The U-value measures the heat transfer through glass. Low-E glass boasts a lower U-value compared to standard glass, highlighting its exceptional potential as a thermal insulator.
SHGC
The solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) is a measure of solar radiation admitted through the glass. Low-E glass is designed to effectively manage solar gain, minimizing cooling energy in summer and heating energy in winter.
VLT
Visible Light Transmission (VLT) measures how much visible light passes through glass, indicating sunlight transmission into indoor spaces. A higher VLT value signifies superior glass performance. Low-E glass maximizes natural light entry while minimizing solar gain, with VLT values ranging from 40% to 70%.
Durability and Maintenance
The metal oxide coatings on Low-E glass are durable and scratch-resistant. It requires no special maintenance and can be cleaned just like standard glass, ensuring it remains clear and performs efficiently.

Low-E Glass Coatings
Low-E glass types are classified based on their coating. These coatings include:
Passive Low-E coatings
Soft Coat (Sputtered): Soft coat, also referred to as the sputtered Low-E coat, is applied to Low-E glass by depositing layers of metal or metal oxide in a vacuum. This coating is highly effective in minimizing heat loss, making it ideal for cold climates. Soft-coated Low-E glass offers superior thermal performance and requires regular, meticulous maintenance.
Solar control Low-E coatings
Hard Coat (Pyrolytic): The hard, or pyrolytic, Low-E coat is applied during glass fabrication while the glass is still hot. This process creates a durable coating that enhances scratch resistance, making it resilient during handling and installation. Hard-coated Low-E glass is commonly used in hot climates to reduce cooling energy needs by reflecting incoming solar heat.
Advantages of Low-E Glass
Low-E glass offers numerous benefits across various industries, including home appliances and construction, such as:
Energy efficiency
Low-E glass significantly reduces heating and cooling energy consumption, resulting in lower energy costs and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. This benefit enhances various features across different applications.
In the home appliance industry, Low-E glass used for oven door interiors plays a crucial role in managing heat and reducing the temperature of the outer oven door glass. This helps minimize energy consumption and lowers the risk of overheating for both the inner and outer oven glasses.

Comfort
Low-E glass enhances comfort in residential and commercial buildings by effectively regulating interior temperatures. It helps maintain a comfortable thermal environment and reduces heat transfer, eliminating cold spots near windows.
UV protection
Low-E glass blocks a significant portion of damaging UV light that can harm furniture, floors, and artworks. This UV protection helps preserve the integrity and appearance of interiors.
Interior light improvement
Low-E glass features high Visible Light Transmission (VLT), enabling ample natural light to enter indoor spaces while reducing solar heat gain. This enhances interior brightness and reduces reliance on artificial lighting during daylight hours.
Applications of Low-E Glass
Low-E glass is versatile and can be used in various applications to enhance both energy efficiency and indoor comfort.
Residential buildings
Low-E glass is commonly installed in windows, skylights, and doors of residential buildings, offering energy savings, enhanced comfort, and improved interior aesthetics for residents.
Commercial buildings
Low-E glass is utilized in the windows of office rooms, atriums, and building facades in commercial structures. This helps enhance the overall energy efficiency of buildings, reduce operational expenses, and improve indoor comfort.
Specialized applications
Low-E glass is also employed in specialized applications including home appliances (for heat management in electric ovens and refrigerators), greenhouses (to regulate temperatures for plant growth), and museums and galleries (providing UV protection for artworks).
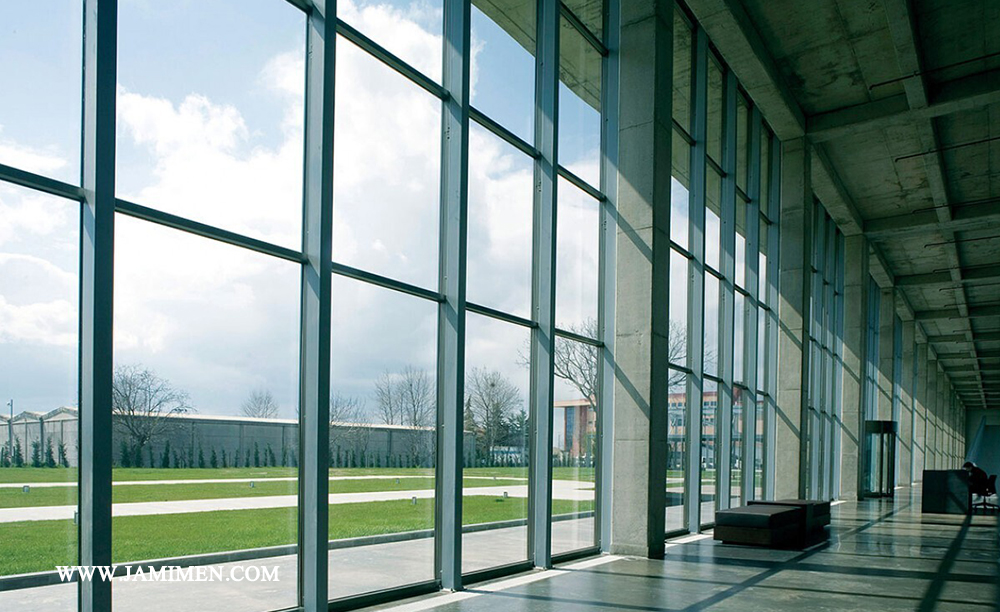

Energy Efficiency Improvement
Enhancing energy efficiency is the primary benefit of Low-E glass. It minimizes heat transfer, maintains thermal comfort, and reduces the need for continuous operation of heating and cooling systems. This results in significant energy savings and a reduced carbon footprint. Studies indicate that buildings equipped with Low-E glass windows can achieve energy savings of up to 30% compared to those with standard glass windows.
Environmental Advantages
In addition to improving energy efficiency, Low-E glass offers significant environmental benefits, such as:
Lower CO2 emission
Low-E glass reduces CO2 emissions from greenhouses by diminishing cooling and heating energy demands. This, in turn, mitigates climate change and contributes to sustainability.
Energy resource protection
Buildings fitted with Low-E glass benefit from enhanced energy efficiency, resulting in reduced consumption of fossil fuels. This supports the conservation of natural resources and encourages the adoption of renewable energy sources.
Challenges and Considerations
While Low-E glass offers numerous advantages, it’s important to consider several challenges and factors:
Investment cost
Low-E glass tends to be more costly than standard glass due to additional production processes and advanced materials. However, the long-term savings on energy costs and the potential increase in property value can outweigh the initial investment.
Installation requirements
Proper installation of Low-E glass is crucial and may necessitate skilled technicians and specific techniques to ensure the integrity of the coatings and effective sealing.
Climatic considerations
The effectiveness of Low-E glass varies depending on the climate. For instance, passive Low-E coatings are highly effective in colder climates, whereas solar control Low-E coatings are more suitable for warmer climates. It is essential to select the appropriate type of Low-E glass based on the specific climate and building requirements.

Advances in Low-E glass technology
Recent advancements in Low-E glass technology continue to enhance their performance and expand their range of applications.
Triple-glazed Low-E glass
Windows equipped with triple-glazed Low-E glass offer significantly improved insulation compared to double-glazed windows. The additional layer between the gas and glass in triple-glazed windows further reduces heat transfer and enhances energy efficiency.
Smart glass
Incorporating Low-E coatings, smart or dynamic glass technologies like electrochromic and thermochromic glasses allow the glass to adjust its characteristics based on environmental conditions. This capability provides dynamic control over heat transfer and light transmission.
Improved coating technologies
Recent advancements in coating technologies have resulted in more efficient and durable Low-E coatings. These innovations, involving new materials and advanced methods, significantly enhance the performance and longevity of Low-E glass, making it more effective in reducing energy consumption.
A structure featuring windows and doors equipped with Low-E glass

Residential Case Study:
House Renovation Focused on Energy Efficiency
Passive Low-E glass windows were installed to enhance energy efficiency during a house renovation in a cold climate. The homeowner noted a 25% reduction in heating costs and improved thermal comfort during winter. Additionally, the Low-E glass contributed to an increase in the resale value of the house due to its improved energy efficiency.
Commercial Case Study: Office Building Strengthening
Solar control Low-E glass was used to replace outdated windows in an office building situated in a warm climate. This initiative reduced cooling expenses by 25% and significantly enhanced thermal comfort. The building’s energy efficiency improved, appealing to tenants who prioritize environmental sustainability.
Specialized Application: Greenhouses
Advanced Low-E glass was integrated into a greenhouse facility to regulate interior temperatures and create optimal conditions for plant growth. It effectively maintained temperatures, reduced energy consumption for heating and cooling, and provided essential UV protection for plants.
Conclusion
Low-E glass stands as a remarkable advancement in glass technology, providing extensive benefits such as improved energy efficiency and comfort in buildings, contributions to home appliances, and advancements in environmental sustainability. Construction professionals and industrial leaders can make informed choices to conserve energy and promote a greener future by understanding the characteristics, varieties, and uses of Low-E glass. As technology progresses, Low-E glass remains pivotal in constructing sustainable, energy-efficient buildings and appliances that achieve high energy efficiency ratings.
Since 2010, Jaam Imen Company has been importing European Low-E glass, processing it to create distinctive products that cater to local needs. Our clients primarily acquire Low-E glass for home appliances, particularly built-in ovens, kitchen ranges, and commercial refrigerators. Jaam Imen Company is proud to enhance the quality of domestically manufactured home appliances in Iran.